
What are the advanced C++ interview questions and answers?
C++ is still as relevant today as it was during its advent in the mid-80s. It’s a powerful general-purpose programming language as it can be used to develop operating systems, browsers, games, etc.
C++ supports different ways of programming like procedural, object-oriented, functional, and so on.
If you want to further improve your C++ language skills, here are some of the best C++ interview questions to help you out.
Create a top-notch C++ developer resume and get matched with C++ developer roles worldwide without compromising privacy.
10 Advanced C++ Interview Questions and Answers
1. What is a mutable storage class specifier? How can it be used?
A mutable storage class specifier is used only on the class’s non-static and non-constant member variables. It’s used for altering the constant class object’s member by declaring it. This can be done by using a storage class specifier.
You can’t use the mutable specifier with names declared as static or const or reference members.

2. What are the differences between a shallow and a deep copy?
| Shallow Copy | Deep Copy |
|---|---|
| It stores the references of objects to the original memory address. | It stores copies of the object’s value. |
| It reflects changes made to the new/copied object in the original object. | It doesn’t reflect changes made to the new/copied object in the original object. |
| It stores the copy of the original object and points the references to the objects. | It stores the copy of the original object and recursively copies the objects as well. |
| It’s faster. | It’s comparatively slower. |
3. What is an abstract class in C++?
An abstract class in C++ is referred to as the base class, which has at least one pure virtual function and is designed to be specifically used as a base class.
You declare a pure virtual function by using a pure specifier ( = 0 ) in the declaration of a virtual member function in the class declaration.

4. Can we have a string primitive data type in C++?
A primitive type is a data type where the values it can represent have a straightforward nature (a number, a character, or a truth value). The primitive types are the most basic building blocks for any programming language and are the base for more complex data types.
We cannot have a String Primitive data type in C++. Instead, we can have a class from the Standard Template Library (STL).
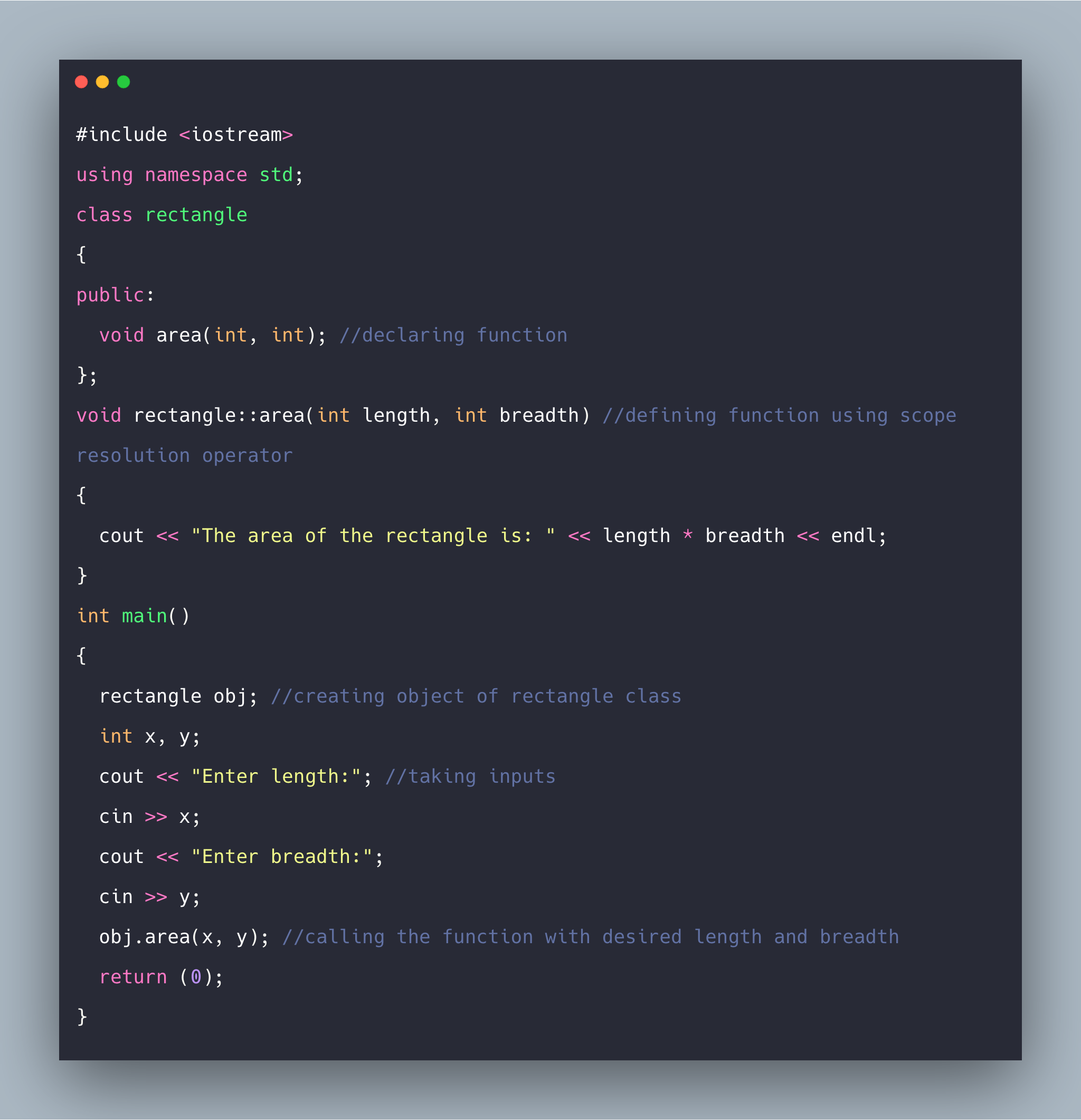
5. What is the function of scope resolution operator in C++?
The scope resolution operator refers to the out-of-scope global variable or member function. It’s denoted by the double colon (::) symbol.
Functions of the scope resolution operator include the following:
They help to resolve the scope of various global variables.
When defined outside the class, a function allows associating the function with the class.
6. What are the C++ tokens?
Generally, a token is an object that represents something else, such as another object (physical or virtual), or an abstract concept, such as a gift, sometimes referred to as a symbol of the giver’s respect for the recipient.
A token is a name given to various functions in C++ programs. Examples of tokens include a keyword, symbol, string literal, identifier, constant, etc.
7. What is the diamond problem?
The diamond problem in C++ occurs when two superclasses of a class have a common base class, representing the inability of the programming language to support hybrid inheritance using multiple and hierarchical inheritances.
8. What is a block scope variable?
Block scope is the definition of a variable within a block of code, such as a for loop or if statement, and a variable specified as a block using C++ that can be declared anywhere within the block.

9. How is the data hiding concept achieved in C++?
Access specifiers define how members of a class (attributes and methods) can be accessed.
C++ supports data hiding and, accordingly, data abstraction and encapsulation by creating user-defined types known as classes. Members of this generated class are scoped by keywords known as access specifiers.
10. What is a “translation unit” in C++?
According to standard C++, a translation unit is the basic compilation unit in C++. It consists of the contents of a single source file and any header file directly or indirectly included in it; lines are ignored by conditional preprocessing statements.
A translation unit consists of:
- Contents of a source file
- Plus contents of files included directly or indirectly
- Minus source code lines ignored by any conditional preprocessing directives ( the lines ignored by #ifdef,#ifndef, etc.)

If you feel prepared for your C++ interviews, now it’s time to meet a job opportunity that’s right for you!
TalentGrid is a platform used by software developers who are actively looking for jobs, allowing them to share their preferences and salary expectations with employers around the world.
By creating your TalentGrid developer profile, you will have an opportunity to be matched with positions worldwide!






